Grasping with LfD algorithms#
Imitation Learning for Low-Cost Dexterous Hand Using RGBD Camera#
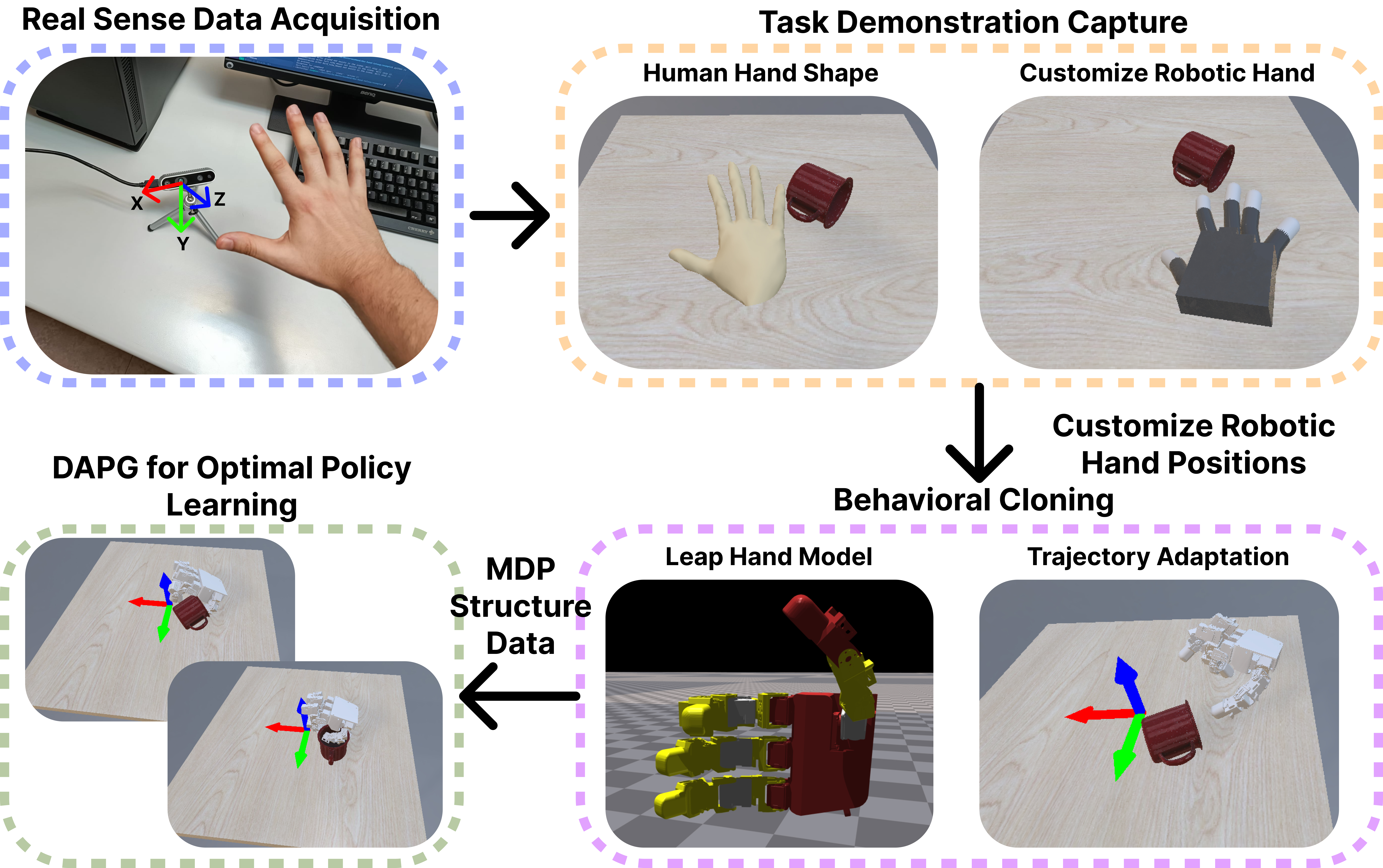
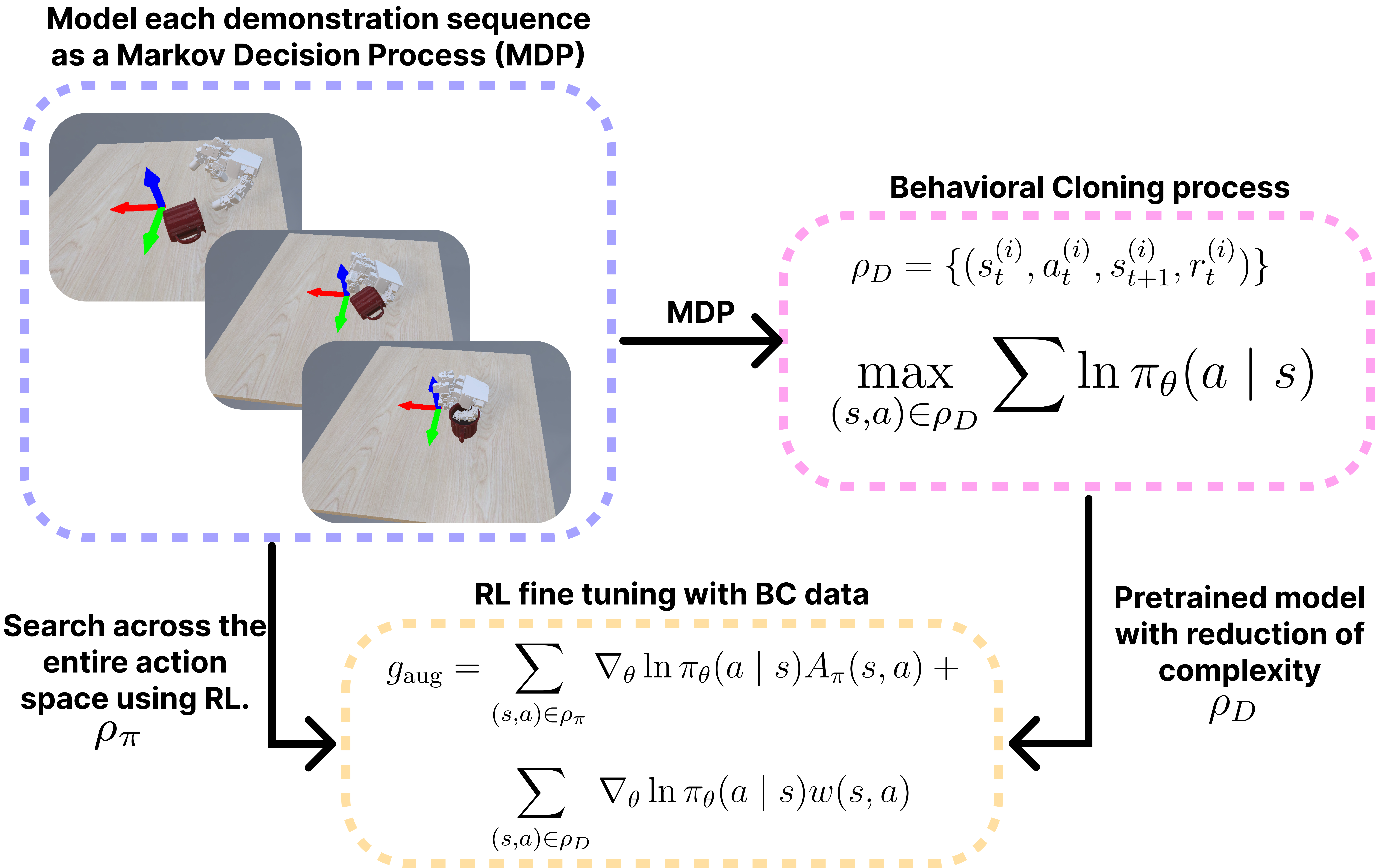
Multi-finger dexterous hands provide robots with a way to perform manipulation tasks in environments adapted for human beings. Their complexity makes the control process a challenging field of research. Techniques such as Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) aim to resolve their control but encounter problems and inefficiencies due to the large number of Degrees of Freedom (DoF) and the system's complexity. This is where the use of Imitation Learning (IL) techniques arises, which rely on human data to perform a learning process that optimizes the search space for an optimal solution. In this work, an IL application is presented for a low-cost dexterous robotic hand, the LEAP Hand. For this purpose, a data collection algorithm is used through the control of a generic robotic hand that adapts to the user's structure and allows the generalization of these demonstrations to any robotic hand. We have implemented a data capture process using an RGBD RealSense camera, which allows controlling the robotic hand. After this, we generate the data structure following a Markov Decision Process (MDP) through a Behavioral Cloning (BC) process, which is used as a basis for training the specific task. For this process, Demo Augmented Policy Gradient (DAPG) is used. To verify the efficiency, the data were collected by different users, and a comparison was made with highly used algorithms within the DRL field, obtaining more robust results in a shorter learning time.
The algorithm focuses on combining an imitation learning process with a reinforcement learning process. These policies are merged using a weight that determines, in each case, which information to prioritize for correctly solving the task. This results in a combined policy capable of performing the task by finding a balance between exploration and exploitation of prior information.